| ☰ See All Chapters |
JDBC Statement
You can create the Statement object as below:
Statement st = con.createStatment();
With Statement, following is the way program executes:
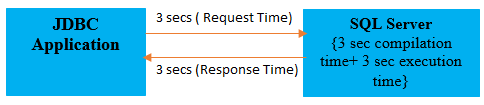
When you submit the query using statement then query will be compiled and executed by the SQL engine every time.
Total time for every request = (request time + compilation time + execution time + response time)
Example: Total time for every request = 3 + 3 + 3 +3 = 12 secs.
DB script
CREATE TABLE EMP(EMP_ID INT(5), NAME VARCHAR(30), SALARY INT(6)); INSERT INTO EMP (EMP_ID,NAME,SALARY) VALUES (103,'Manu',3000); INSERT INTO EMP (EMP_ID,NAME,SALARY) VALUES(104,'Tyagraj',4000); INSERT INTO EMP (EMP_ID,NAME,SALARY) VALUES(105,'Likitha',5000); INSERT INTO EMP (EMP_ID,NAME,SALARY) VALUES(106,'Advith',6000); COMMIT; |
JdbcMysqlDemo.java
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement;
public class JdbcMysqlDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection con = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet rs = null;
try { //Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //for mysql versions lesser than 8.0 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//for mysql version 8.0
System.out.println("Driver is loaded"); con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/study", "root", "root"); System.out.println("got database connection"); st = con.createStatement();
// Preparing Batch // (queries affects single rows) st.addBatch("INSERT INTO EMP (EMP_ID, NAME,SALARY) VALUES(108,'JEEVAN',8000)"); st.addBatch("UPDATE EMP SET SALARY=3333 WHERE NAME = 'GANESH'"); st.addBatch("DELETE FROM EMP WHERE EMP_ID=104");
// (queries affects multiple rows) st.addBatch("UPDATE EMP SET SALARY=9999 WHERE EMP_ID > 106"); st.addBatch("DELETE FROM EMP WHERE EMP_ID < 104");
// executebatch for execution of SQL queries(CUD) int a[] = st.executeBatch(); System.out.println("Value of a for executing batch is " + a.length);
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.println(a[i]); } // executeUpdate() method for execution of SQL queries (CUD) int p = st.executeUpdate("UPDATE EMP SET SALARY=9999 WHERE EMP_ID > 106"); int q = st.executeUpdate("DELETE FROM EMP WHERE EMP_ID < 104"); System.out.println("Value of p for updating multiple rows" + p); System.out.println("Value of q for deleting multiple rows " + q);
// execute() method for execution of SQL queries (CRUD) boolean x = st.execute("INSERT INTO EMP (EMP_ID, NAME,SALARY) VALUES(108,'JEEVAN',8000)"); boolean y = st.execute("UPDATE EMP SET SALARY=3333 WHERE NAME = 'GANESH'"); System.out.println("Value of x for inserting one row is " + x); System.out.println("Value of y for updating one row is " + y);
// executeQuery() method for execution of SQL queries (R) rs = st.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM EMP");
while (rs.next()) { System.out.print(rs.getInt("EMP_ID") + "\t"); System.out.print(rs.getString("NAME") + "\t"); System.out.println(rs.getString("SALARY")); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("Exception caught: " + e); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("Exception caught: " + e); e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (rs != null) { rs.close(); } if (st != null) { st.close(); } if (con != null) { con.close(); } } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("Error in closing resources: " + e); e.printStackTrace(); } } } } |
Output
Driver is loaded got database connection Value of a for executing batch is 5 1 0 1 1 1 Value of p for updating multiple rows1 Value of q for deleting multiple rows 0 Value of x for inserting one row is false Value of y for updating one row is false 103 Manu 3000 104 Tyagraj 4000 105 Likitha 5000 106 Advith 6000 |
All Chapters

