Write and Publish a Tutorial!
Do you have good notes or papers written by you and seeking for a
platform to publish? We provide the platform to publish your tutorials
in your name. If you wish to publish your tutorial in your name to
help the readers, Please contact us by sending an email to
publish@tools4testing.com or publish@java4coding.com The main way that
others learn about your work is through your published tutorials. If
you don’t publish, it will be as if you never did the work. Your notes
can help the readers only when you share it.
Implementing Custom Authentication in Spring Security by Overriding AuthenticationProvider
In enterprise applications, you may encounter situations where the default username and password authentication method doesn't fit your needs. Sometimes, you might require various authentication methods, such as using a code from an SMS or a specific application, or even utilizing a user's fingerprint for authentication. To handle these scenarios, Spring Security allows you to implement custom authentication logic using the Authentication interface and an AuthenticationProvider.
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
Object getCredentials();
Object getDetails();
Object getPrincipal();
boolean isAuthenticated();
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}
The Authentication interface represents the authentication request event and contains details about the entity requesting access to the application, known as the principal. Key methods in this interface include:
isAuthenticated(): Indicates if the authentication process is complete.
getCredentials(): Provides the password or secret used in authentication.
getAuthorities(): Returns the granted authorities for the authenticated request.
getDetails(): Provides additional details about the request, if needed.
The AuthenticationProvider interface defines how authentication is performed. It typically delegates user retrieval to a UserDetailsService and handles password management with a PasswordEncoder. You implement the authenticate() method to validate the authentication request, returning an authenticated object. The supports() method indicates if the AuthenticationProvider supports a particular authentication object.
To summarize, implementing authenticate() involves:
Throwing AuthenticationException if authentication fails.
Returning null if the authentication object isn't supported.
Returning a fully authenticated Authentication instance.
The supports() method helps Spring Security to determine which AuthenticationProvider to use based on the authentication object. This flexible approach allows for rejecting authentication requests based on various criteria.
Imagine a secure vault with multiple locks, each requiring a different type of key to open. Each key represents a different authentication method: one for fingerprints, another for access cards, and a third for numerical codes. The vault manager (authentication manager) determines which lock (authentication provider) to engage based on the type of key presented. If someone tries to use a fingerprint key at the access card lock, it won't work. However, if the access card lock is selected, it will validate the access card accordingly. This setup ensures robust security while accommodating diverse access methods.
Besides testing the authentication type, Spring Security adds one more layer for flexibility. The access card lock can recognize multiple kinds of cards. In this case, when you present a card, one of the authentication providers could say, “I understand this as being a card. But it isn’t the type of card I can validate!” This happens when supports() returns true but authenticate() returns null.
Example
In the below example we implement username and password authentication method which is same as default authentication approach.
pom.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="https://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.0</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository, not local -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.java4coding</groupId>
<artifactId>ImplementingCustomAuthentication </artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>ImplementingCustomAuthentication </name>
<description>Implementing Custom Authentication in Spring Security by Overriding AuthenticationProvider</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<spring-boot.version>2.6.0</spring-boot.version>
<lombok.version>1.18.28</lombok.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>build-info</id>
<goals>
<goal>build-info</goal>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project> |
SpringBootDemo.javapackage com.java4coding;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
@SpringBootApplication
@EntityScan
@EnableJpaRepositories
public class SpringBootDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemo.class, args);
}
} |
ApplicationConfig.javapackage com.java4coding.config;
import com.java4coding.repository.UserRepository;
import com.java4coding.security.UserDetailsServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.NoOpPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
@Configuration
public class ApplicationConfig {
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService(UserRepository userRepository) {
return new UserDetailsServiceImpl(userRepository);
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
} |
ApplicationWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.javapackage com.java4coding.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
public class ApplicationWebSecurityConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider;
/*
Since H2 has its own authentication provider, you can skip the Spring Security for the
path of h2 console entirely in the same way that you do for your static content.
In order to do that, in your Spring security config, you have to override the configuration
method which takes an instance of org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.WebSecurity
as a parameter instead of the one which takes an instance of org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity
*/
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring().antMatchers("/h2-console/**");
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) {
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);
}
} |
DemoController.javapackage com.java4coding.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@GetMapping(value = "/demo")
public String sayHello() {
return "Hurray! You are Authorized.";
}
} |
User.javapackage com.java4coding.entity;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
@Setter
@Getter
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String authority;
} |
UserRepository.javapackage com.java4coding.repository;
import com.java4coding.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
List<User> findByUsername(String userName);
} |
CustomAuthenticationProvider.javapackage com.java4coding.security;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) {
String username = authentication.getName();
String password = authentication.getCredentials().toString();
UserDetails user = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username);
if (passwordEncoder.matches(password, user.getPassword())) {
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password, user.getAuthorities());
} else {
throw new BadCredentialsException("Something went wrong!");
}
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authenticationType) {
return UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authenticationType);
}
} |
SecurityUser.javapackage com.java4coding.security;
import com.java4coding.entity.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
public class SecurityUser implements UserDetails {
private final User user;
public SecurityUser(User user) {
this.user = user;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return user.getUsername();
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return user.getPassword();
}
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return List.of(() -> user.getAuthority());
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return true;
}
} |
UserDetailsServiceImpl.javapackage com.java4coding.security;
import com.java4coding.entity.User;
import com.java4coding.repository.UserRepository;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import java.util.List;
@AllArgsConstructor
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public SecurityUser loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
List<User> usersByUserName = userRepository.findByUsername(username);
return new SecurityUser(usersByUserName.get(0));
}
} |
application.propertiesspring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.h2.console.path=/h2-console/
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=pass
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
#spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create-drop
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show_sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.use_sql_comments=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true |
schema.sqlcreate table user (
id bigint generated by default as identity,
authority varchar(255),
password varchar(255),
username varchar(255),
primary key (id)
); |
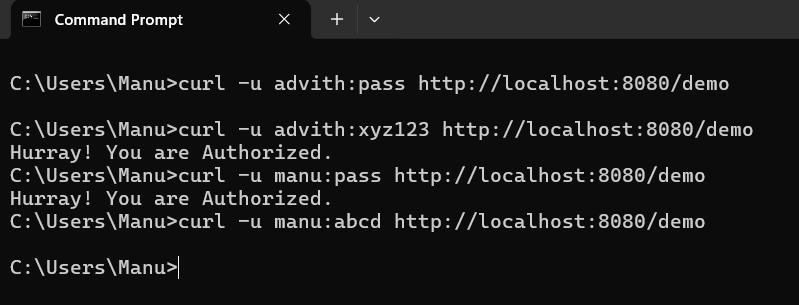
data.sqlINSERT INTO User (id, username, password, authority) VALUES (1, 'manu', 'pass', 'read');
INSERT INTO User (id, username, password, authority) VALUES (2, 'advith', 'xyz123', 'read');
INSERT INTO User (id, username, password, authority) VALUES (3, 'aashvith', 'xyz123', 'read'); |
Project Structure
Output