| ☰ See All Chapters |
Java Set
Set models the mathematical set abstraction.
Contains no methods other than those inherited from Collection.
Two Set objects are equal if they contain the same elements.
Lists are usually used to keep things in some kind of order, Lists allow you to manually override the ordering of elements by adding or removing elements via the element's index.
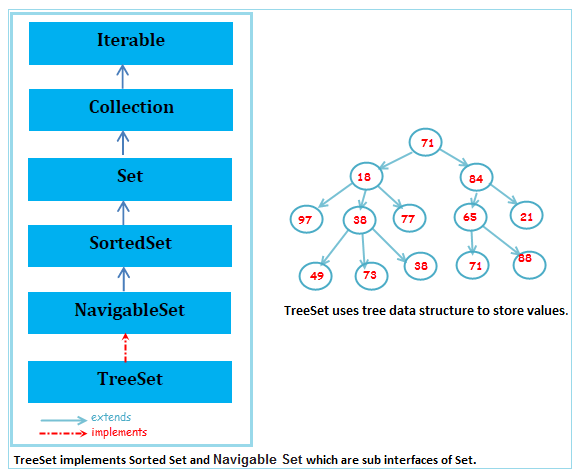
Set has 3 different implementations
TreeSet
HashSet
LinkedHashSet
TreeSet
TreeSet implements SortedSet which is sub interface of Set.
Elements in TreeSet are sorted by natural ascending order or custom comparision rules.
Null value is not allowed.
Duplicates and dissimilar objects are not allowed.
Elements cannot be access randomly.
TreeSet uses tree data structure to store values.
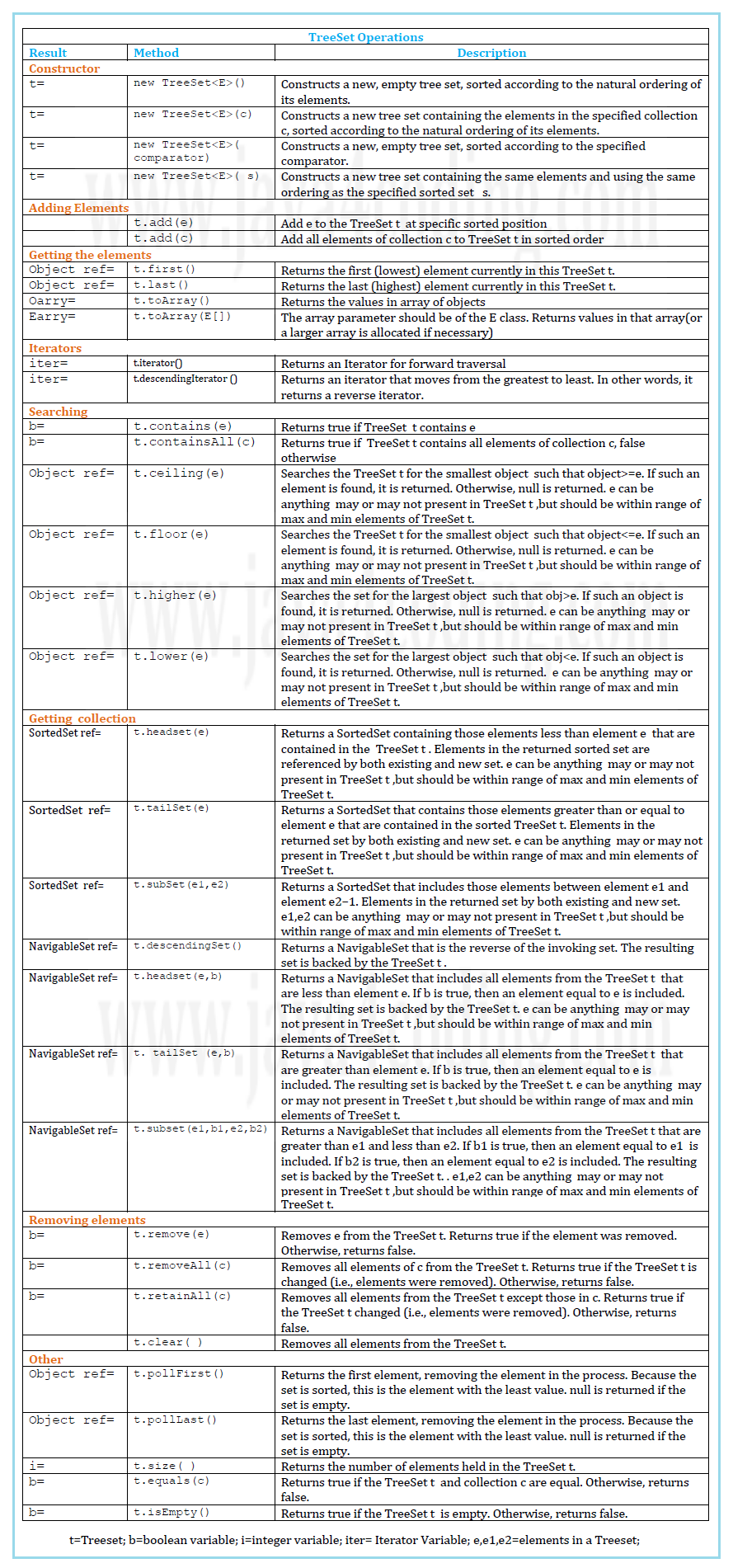
TreeSet Example
TreeSetDemo.java
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.NavigableSet; import java.util.SortedSet; import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TreeSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a TreeSet TreeSet set1 = new TreeSet(); TreeSet set2 = new TreeSet(); TreeSet<Integer> set3 = new TreeSet();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); list.add(10); list.add(20); list.add(30); list.add(40);
// Adding Elements to TreeSet set1.add(30); set1.add(40); set1.add(10); set1.add(20);
set2.addAll(list); set3.addAll(list); // cannot add duplicates, dissimilar and null values in TreeSet
// set.add("A"); // set.add(new Integer(10)); // set.add(null); System.out.println("Contents of TreeSet set1: " + set1); System.out.println("Contents of TreeSet set2: " + set2); System.out.println("Contents of TreeSet set3: " + set3);
// Getting the elements Object o1[] = set1.toArray(); System.out.println(o1[0]); Integer i1 = (Integer) o1[2]; System.out.println(i1);
Integer i2[] = set3.toArray(new Integer[set3.size()]);// getting exactly same size as set3 Integer i3[] = set3.toArray(new Integer[5]);// specifying size explicitly
Object o2 = set1.first(); System.out.println(o2); Object o3 = set1.last(); System.out.println(o3);
// Searching boolean b1 = set1.contains(10); System.out.println(b1); boolean b2 = set1.containsAll(set2); System.out.println(b1); Object o4 = set1.ceiling(25); System.out.println(o4); Object o5 = set1.floor(25); System.out.println(o5); Object o6 = set1.higher(25); System.out.println(o6); Object o7 = set1.lower(25); System.out.println(o7);
// Getting collection SortedSet ref1 = set1.headSet(35); System.out.println(ref1); SortedSet ref2 = set1.tailSet(35); System.out.println(ref2); SortedSet ref3 = set1.subSet(15, 35); System.out.println(ref3); NavigableSet ref4 = set1.descendingSet(); NavigableSet ref5 = set1.headSet(35, true); System.out.println(ref5); NavigableSet ref6 = set1.tailSet(35, false); System.out.println(ref6); NavigableSet ref7 = set1.subSet(15, true, 35, false); System.out.println(ref7);
// Removing elements boolean b3 = set1.remove(30); System.out.println(b3); boolean b4 = set2.removeAll(set1); System.out.println(b4); boolean b5 = set2.retainAll(set1); System.out.println(b5); set2.clear();
// Other Object o8 = set1.pollFirst();// Returns the first element, removing the element in the process System.out.println(set1); Object o9 = set1.pollLast();// Returns the last element, removing the element in the process System.out.println(set1); int i = set1.size(); System.out.println(i); boolean b7 = set1.equals(set2); System.out.println(b7); boolean b8 = set1.isEmpty(); System.out.println(b8); } } |
Output:
Contents of TreeSet set1: [10, 20, 30, 40] Contents of TreeSet set2: [10, 20, 30, 40] Contents of TreeSet set3: [10, 20, 30, 40] 10 30 10 40 true true 30 20 30 20 [10, 20, 30] [40] [20, 30] [10, 20, 30] [40] [20, 30] true true true [20, 40] [20] 1 false false |
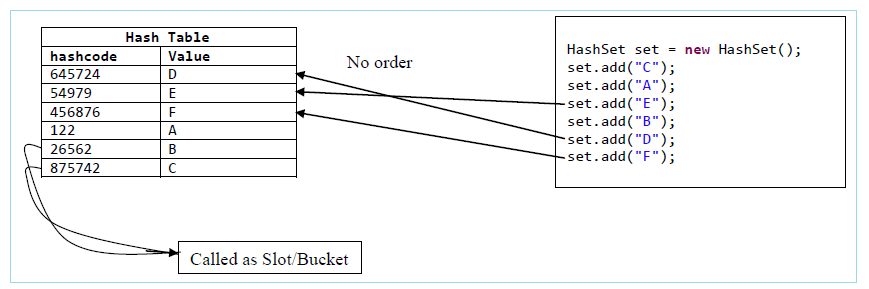
HashSet
HashSet stores the elements in a hash table.
It uses the hash code of the object being inserted.
Hash table is also a data structure which can be used for storing values.
The values in the hash table are always stored after generating the hash code for that value.
The mechanism of generating the hash code for a value is called hashing technique. In java hashCode() method provides the support for generating the hash code.
HashSet defines no any extra methods other than those inherited from Collection Interface.
LinkedHashSet
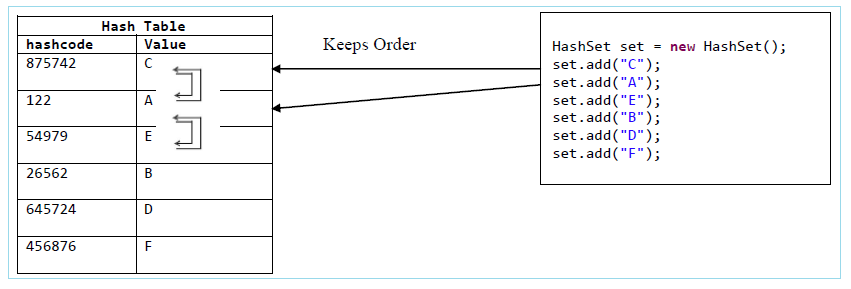
LinkedHashSet has a combined implementation of hash table and linked list.
LinkedHashSet stores elements in a hash table and links them with double linked list.
Values are stored in the same order as inserted and are unsorted.
LinkedHashSet defines no any extra methods other than those inherited from Collection Interface.
All Chapters

