| ☰ See All Chapters |
String handling in Java
Creating String Object
There are two ways to create String object:
By string literal
By new keyword
By string literal | By new keyword |
String literal is created by double quote. String s = "Hello"; | String literal is created by using new key word. String s = new String("Welcome"); |
Each time you create a string literal, the JVM first checks the string constant pool. If the string already exists in the pool, a reference to the pooled instance returns. If the string does not exist in the pool, a new String object instantiates then is placed in the pool. | JVM will create a new String object in normal Heap memory. The variable will refer to the object in Heap. |
Applicable only for String class. (Not applicable for StringBuilder, StringBuffer classes.) | Applicable for String , StringBuilder, StringBuffer classes. |
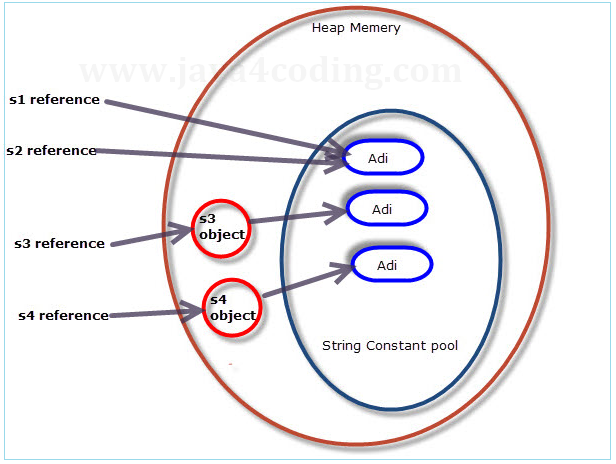
Consider below code with four different string variables s1, s2, s3, s4 assigned with string values. Let us see what happens inside.
package com.java4coding;
public class StringHandling { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = "Adi"; String s2 = "Adi String s3 = new String("Adi"); StringBuilder s4 = new StringBuilder("Adi"); } } |
String s1 = "Adi"; | New String Constant created in string constant pool, s1 is returned to this. |
String s2 = "Adi | No new object is created, s2 is returned with the same above string present in string constant pool. |
String s3 = new String("Adi"); | JVM will create a new String object in Heap memory and the literal "Adi" will be placed in the string constant pool. The variable s3 will refer to the object in Heap. |
StringBuilder s4 = new StringBuilder("Adi"); | JVM will create a new String object in Heap memory and the literal "Adi" will be placed in the string constant pool. The variable s4 will refer to the object in Heap. |
Mutability concept
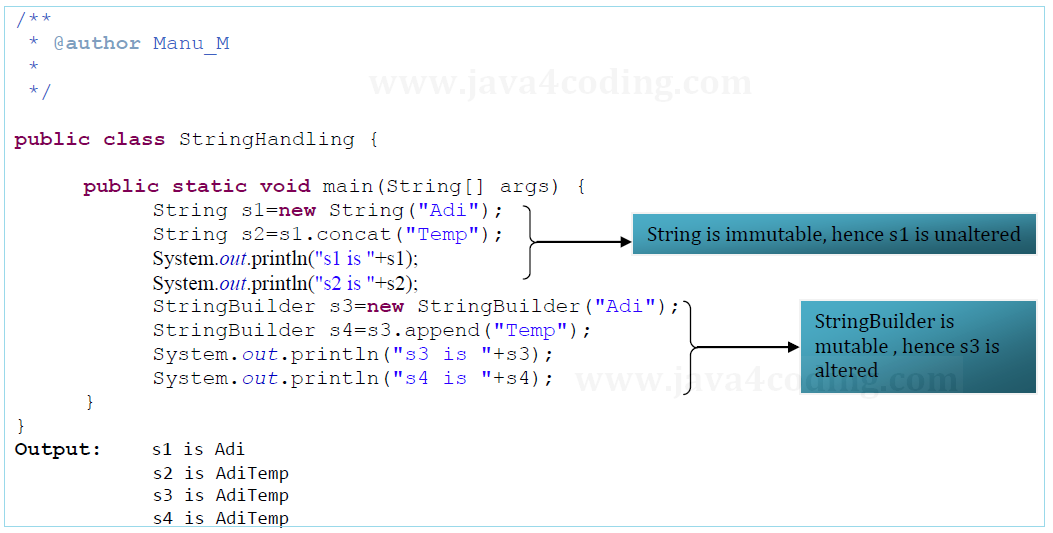
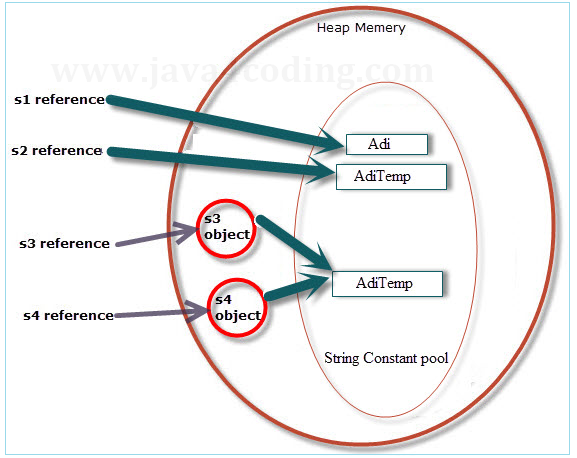
String class is immutable. StringBuffer and StringBuilder classes are mutable (modifiable) strings.
Let's try to understand the immutability concept by the example given below:
All Chapters

